本文最后更新于 2023-01-13 ,文中内容可能已过时。
注意:不可变数据类型在修改时会创建一个新对象
特点:
1
2
print ( " %s , %s , %s " % ( 't1' , '2' , '3' )) # 格式化
# print(f'myname:{name}') # py2不支持
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# list
name = 'raja'
print ( '-' . join ([ '2' , '3' , '4' ])) # 拼接
f1 = [ '1' , '2' , '3' ]
f2 = list ( f1 )
f1 . append ( '4' )
f3 = [ list ( f1 ) for i in range ( 3 ) if i % 2 == 0 ]
print ( f3 )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# tuple: 是否可变需要看内部成员对象
sql = ( 1 , [])
sql [ - 1 ] . append ( 1 )
print ( sql )
# 结合一下
a_string = 'abc汉字'
a_list = list ( a_string )
a_tuple = tuple ( a_list )
a_string2 = '' . join ( a_tuple )
print ( a_string , a_list , a_tuple , a_string2 )
for char in a_string :
print ( char , end = ' ' )
for ele in a_list :
print ( ele )
else :
print ( "none" )
for idx , char in enumerate ( a_string ): # idx,elem
print ( idx , char )
s = "asdasd sadasda asdasdadas"
# 转码:
"""
for ch in s:
if 'a' <= ch <= 'z':
ch = chr((ord(ch) - ord('a') + 2) % 26 + ord('a'))
print(ch, end='')
"""
print ( "" . join ([ chr (( ord ( ch ) - ord ( 'a' ) + 2 ) % 26 + ord ( 'a' )) if 'a' <= ch <= 'z' else ch for ch in s ]))
1
2
3
4
5
6
# dict
a_dict = { 'a' : '1' , 2 : 'b' }
print ( a_dict . keys (), a_dict . values (), a_dict . items ())
print ( a_dict . get ( 1 ))
print ( a_dict . pop ( 2 )) # key必须存在
a_dict . clear ()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# set
a_set = set () # 空set 不能用{}:表示字典
b_set = set ()
for i in range ( 10 ):
a_set . add ( random . Random () . randint ( 1 , 20 ))
b_set . add ( random . Random () . randint ( 10 , 30 ))
print ( a_set & b_set , a_set | b_set , a_set - b_set , a_set ^ b_set )
a_set . update ({ "set" }) # 更新一个字符串到集合
a_set . update ( "set" ) # 将字符串拆分为字符再进行添加
print ( a_set )
# 去重
b_list = [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 1 , 3 , 5 ]
b_list = list ( set ( b_list ))
print ( b_list )
注意:
对于是字典和字符转换的集合是随机删除元素,当集合是由列表和元组组成时,set.pop()是从最左边删除
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# 文件
# with open('test.txy') as f:
# for line in f:
# print(line)
# 读取csv文件
import csv
rows = [[ 'jack' , 18 , 'Male' ], [ 'boss' , 20 , 'Female' ]]
with open ( 'data.csv' , newline = '' , mode = 'a' ) as out_csv :
file_writer = csv . writer ( out_csv )
file_writer . writerows ( rows )
with open ( 'data.csv' , newline = '' , mode = 'r' ) as in_csv :
file_reader = csv . reader ( in_csv )
header = next ( file_reader )
print ( file_reader . line_num , header )
for row in file_reader :
print ( row )
# csv 文件处理
# with open('marks.csv', newline='', mode='r') as in_csv:
# file_reader = csv.DictReader(in_csv)
# header = file_reader.fieldnames
# header.append('total')
# with open('marks_new.csv', newline='', mode='r') as out_csv:
# file_writer = csv.DictWriter(out_csv, header)
# for row in file_reader:
# total = (eval(row['math']) + eval(row['english']))
# row['total'] = int(total)
# file_writer.writerow(row)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
import json
test_dict = { 'name' : 'Tom' , 'age' : 20 , 'hobby' : [ 'swimming' , 'reading' , 'jogging' ], 'married' : False }
json_str = json . dumps ( test_dict ) # 串行花
print ( type ( json_str ))
print ( json_str )
json_dict_new = json . loads ( json_str ) # 解码
print ( json_dict_new == test_dict )
with open ( 'data.json' , 'w' ) as jf :
json . dump ( test_dict , fp = jf , indent = 4 ) # map转json文件(带格式)
with open ( 'data.json' , 'r' ) as jf :
new_dict = json . load ( jf )
print ( type ( new_dict ), new_dict )
# 自定义类的串行化
def encode_user ( o ):
if isinstance ( o , User ):
return { 'name' : o . name , 'age' : o . age , o . __class__ . __name__ : True }
else :
raise TypeError ( 'error' )
class User :
def __init__ ( self , name , age ):
self . name = name
self . age = age
user = User ( 'raja' , 21 )
json_user = json . dumps ( user , default = encode_user ) # 先转为map,再转为json
print ( json_user )
# 自定义类的反串行化
def decode_user ( o ):
if isinstance ( o , dict ):
if User . __name__ in o :
return User ( o [ 'name' ], o [ 'age' ])
raise TypeError ( 'error' )
print ( json . loads ( json_user ))
print ( type ( json . loads ( json_user , object_hook = decode_user )))
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 函数
def func ( a , * args , ** kwargs ): # 变量,可变参,map
print ( a , args , kwargs )
print ( datetime . datetime ( ** kwargs )) # 对字典做拆分
print ( list ( range ( * args ))) # 起点,终点,步长
func ( 1 , 0 , 10 , 2 , year = 2002 , month = 3 , day = 26 )
def func2 ( x , y , z = 4 , * param , ** params ):
print ( x , y , z )
print ( param )
print ( params )
for i in range ( len ( param )):
print ( i , ":" , param [ i ])
for k in params :
print ( k , ":" , params [ k ])
func2 ( 1 , 2 , 1 , 2 , 3 , a = 1 , b = 2 )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
from functools import reduce
a = [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]
filter_result = list ( filter ( lambda x : x % 2 == 0 , a )) # 过滤器
map_result = list ( map ( lambda x : x ** x , a )) # 对每个值进行操作
reduce_result = reduce ( lambda a , b : a + b , a , 0 ) # 累加函数,输入列表,初始值
print ( filter_result , map_result , reduce_result )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
from collections import *
# 命名tuple
User = namedtuple ( 'User' , [ 'name' , 'age' , 'sex' ])
u = User ( 'Tom' , 20 , 'Male' )
print ( u . name , u . age , u . sex )
# 双端队列
q = deque ([ 'u' , 'v' , 'w' ])
q . append ( 'z' )
q . appendleft ( 'a' )
q . remove ( 'u' )
print ( q )
# 计数:dict的子类用于计数可hash对象,以map的k-v对形式存储u,当访问的key不存在时返回0,否则返回计数
cnt = Counter ( 'abcdabdssad' )
print ( cnt , cnt [ 'a' ], cnt [ 'b' ], cnt [ 'z' ])
# 有序字典:dict的子类,按照插入的顺序排列
od = OrderedDict ([( 'a' , 1 ), ( 'b' , 2 ), ( 'c' , 3 )])
print ( od )
# 默认值字典:不存在的key返回默认值
dd = defaultdict ( lambda : 'N/A' )
dd [ 'k1' ] = 'red'
print ( dd [ 'k1' ], dd [ 'k2' ], dd . get ( 'k2' , None ))
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 迭代器
import itertools
# 无限迭代器
for i in itertools . count ( 1 , 1 ): # 从当前数字无限循环下去
print ( i )
for i in itertools . cycle ([ 1 , 2 , 3 ]): # 无限滚动循环传入的序列
print ( i )
for i in itertools . repeat ( 'a' , 5 ): # 可以循环指定元素(可以指定个数)
print ( i )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 有限迭代器
# 将一组迭代对象串联为一个大的迭代器
for i in itertools . chain ( 'abcde' , 'de' ):
print ( i )
# 相邻的元素根据age进行分组
persons = [{ 'name' : 'Tom' , 'age' : 20 }, { 'name' : 'Bob' , 'age' : 19 }, { 'name' : 'Alice' , 'age' : 20 },
{ 'name' : 'Bess' , 'age' : 20 }]
for key , grp in itertools . groupby ( persons , key = lambda x : x [ 'age' ]):
print ( key , list ( grp ))
# 计算迭代器:默认累加求和
for i in itertools . accumulate ([ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]):
print ( i , end = ' ' )
print ()
for i in itertools . accumulate ([ 1 , 2 , 5 , 3 , 2 ], max ):
print ( i , end = ' ' )
print ()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 组合迭代器
# 可迭代的笛卡儿积
for i in itertools . product ([ 1 , 2 , 3 ], [ 4 , 5 , 6 ], [ 4 , 5 ]):
print ( i , end = ' ' )
print ()
# 全排列 长度为2 无重复元素
for i in itertools . permutations ( 'abc' , 2 ):
print ( i , end = ' ' )
print ()
# 组合 有序 无重复元素
for i in itertools . combinations ( 'abc' , 2 ):
print ( i , end = ' ' )
print ()
# 长度为2的组合,有序,可重复
for i in itertools . combinations_with_replacement ( 'abc' , 2 ):
print ( i , end = ' ' )
print ()
源码安装
在源码包根路径下python setup.py install
包管理器自动安装
pip install django==2.2.1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# 封装
class Person :
"""this is a people class esample"""
person_name = [ 1 , 2 , 3 ] # 类属性 公共模板 赋值会单独拥有,修改内容会同时修改
def __init__ ( self ):
self . name = None # 每个实例单独的
def speak ( self , name ):
self . name = name
print ( 'name:' , self . person_name , ':' , self . name )
p1 = Person ()
p1 . speak ( 'test' )
p2 = Person ()
print ( dir ( p1 )) # 方法和属性
print ( type ( p1 )) # 类信息
p1 . person_name [ 0 ] = - 1 # 修改内容会导致所有实例都被修改
print ( p1 . person_name )
print ( p2 . person_name )
p1 . person_name = [ 2 , 3 , 4 ] # 直接赋值只改变自身
print ( p1 . person_name )
print ( p2 . person_name )
print ( p1 . __dict__ ) # 动态语言 动态增加删除类属性
p1 . test = 'test'
del p1 . name
print ( p1 . __dict__ )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
# 继承
class Student ( Person ): # 继承父类的属性和方法
def __init__ ( self , name , food , grade , age = 21 ):
super () . __init__ ( name , age )
self . food = food
self . grade = grade
def eat ( self , food ):
print ( 'eat:' , food )
def speak ( self ): # 方法重写
super ( Student , self ) . speak () # 调用父类的方法
print ( 'name:' , self . person_name , ':' , self . name )
s1 = Student ( 'raja' , 'apple' , 90 , '21' )
print ( dir ( s1 ))
print ( s1 . name , s1 . person_name )
s1 . speak ()
# 多继承
class Runner :
def __init__ ( self , mode ):
self . mode = mode
def run ( self , speed ):
print ( 'run:' , speed , 'mode:' , self . mode )
def speak ( self ):
print ( 'speak:' , self . mode )
class MuxPerson ( Person , Runner ):
def __init__ ( self , mux , name , age , mode ):
super () . __init__ ( name , age ) # 通过调用父类名进行初始化
Runner . __init__ ( self , mode )
self . mux = mux
def mux ( self ):
print ( 'mux:' , self . mux )
mp = MuxPerson ( 'raja' , 21 , 'normal' )
print ( MuxPerson . __mro__ ) # 方法解析顺序
print ( MuxPerson . __bases__ ) # 直接父类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 多态
def func ( * persons ):
for person in persons :
person . speak () # 尝试调用,子类没有寻找父类
# 判断person对象是否是Person或其子类
print ( type ( person ), isinstance ( person , Person ))
p1 = Person ( 'raja' , 21 )
p2 = Runner ( 'normal' )
func ( p1 , p2 )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 类的私有属性和方法(非严格意义)
class Private :
__grade = 100 # 私有属性
def __speak ( self ): # 私有方法
print ( 'private:' , self . __grade )
# def _Private__speak(self, name): # 无法访问
# print('hhh:', name)
def Run ( self ):
self . __speak ()
private = Private ()
print ( dir ( private ))
private . Run ()
# 直接调用私有化
print ( private . _Private__grade )
private . _Private__speak ()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 类的静态方法和实例方法
class StaticClass :
name = 'raja'
def __init__ ( self , age = 21 ) -> None :
print ( 'init' )
self . age = age
def set_age ( self , age ):
self . age = age
@staticmethod # 静态方法:可以直接通过类名进行调用
def static_method ( name ):
print ( 'static_method:' , name )
@classmethod # 类方法:特殊的静态方法:可以调用类自身的属性和方法
def class_method ( cls ):
cls . __init__ ( cls ) # 默认不会调用init方法
cls . set_age ( cls , 20 )
print ( 'class_method:' , cls . name , cls . age )
StaticClass . static_method ( 'raja' )
StaticClass . class_method ()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# 类的内置属性和方法
class Vector :
"""定义了向量及其加法"""
def __init__ ( self , x , y ):
self . x = x
self . y = y
def __repr__ ( self ) -> str : # 面向调试者
return '( %d , %d )' % ( self . x , self . y )
def __str__ ( self ) -> str : # 面向程序使用者
return '( %d , %d )' % ( self . x , self . y )
def __add__ ( self , other ):
return Vector ( self . x + other . x , self . y + other . y )
print ( 'doc:' , Vector . __doc__ )
print ( 'name:' , Vector . __name__ )
print ( 'module:' , Vector . __module__ ) # 所在模块
print ( 'bases:' , Vector . __bases__ )
print ( 'dict:' , Vector . __dict__ )
"""
doc: 定义了向量及其加法
name: Vector
module: __main__
bases: (<class 'object'>,)
dict: {'__module__': '__main__', '__doc__': '定义了向量及其加法', '__init__': <function Vector.__init__ at 0x7fe3a77b8790>, '__repr__': <function Vector.__repr__ at 0x7fe3a77b8820>, '__add__': <function Vector.__add__ at 0x7fe3a77b88b0>, '__dict__': <attribute '__dict__' of 'Vector' objects>, '__weakref__': <attribute '__weakref__' of 'Vector' objects>}
"""
注意 :python本身不支持方法重载,但可以看这篇文章 了解另类实现.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
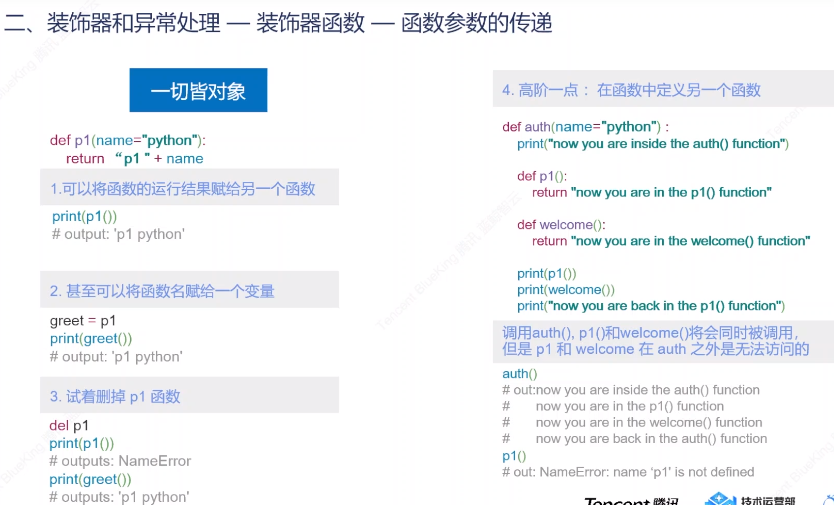
# 函数参数传递
def func ( doing ):
data = [ 1 , 3 , 4 ]
@functools . wraps ( doing ) # 记录并加入复制函数的名称,注释文档,参数列表,保证doing.__name__不被更改
def inner ():
print ( "pre" )
data . append ( - 1 ) # 函数闭包:会携带引用对象
doing ( data )
print ( "next" )
return inner
def doing ( data ): return print ( "doing:" , data )
f = func ( doing )
f () # doing: [1, 3, 4, -1]
f () # doing: [1, 3, 4, -1, -1]
func ( doing )() # doing: [1, 3, 4, -1]
func ( doing )() # doing: [1, 3, 4, -1]
# 简写:注释
@func # 相当于 doing2 = func(doing2)
def doing2 ( * args ): return doing ( * args )
doing2 ()
print ( doing2 . __name__ )
"""
next
pre
doing: [1, 3, 4, -1]
next
doing2
"""
解决函数名称被更改的问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 装饰器可以带参数(完整版)
def logging ( level ): # 需要再嵌套一层
def out_wrapper ( func ):
@functools . wraps ( func )
def wrapper ( * args , ** kwargs ):
print ( "[ {} ]:enter: {} ()" . format ( level , func . __name__ ))
return wrapper
return out_wrapper
level = 'info'
@logging ( level ) # @out_wrapper : hello=out_wrapper(hello)
def hello ( a , b , c ):
print ( a , b , c )
print ( hello . __name__ )
hello ( 1 , 2 , 3 )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# 装饰器类
class Decs ( object ):
def __init__ ( self , name ) -> None :
self . name = name
def __call__ ( self , func ):
@functools . wraps ( func )
def inner ( * args , ** kwargs ):
print ( "before function:" , self . name )
result = func ( * args , ** kwargs )
print ( "after function:" , self . name )
return result
return inner
@Decs ( 'raja' ) # 等价于 func = Decs().__call__(func); func = Decs()(func)
def func (): print ( "func()" )
func ()
print ( func . __name__ )
"""
before function
func()
after function
func
"""
创建和读取压缩包
文件,文件夹,压缩包处理模块
完整代码